The age-old debate between centralized and decentralized procurement continues to shape organizational strategies. While both approaches offer distinct advantages, the optimal solution often lies in a hybrid model that balances control, flexibility, and efficiency.
Centralized Procurement
In a centralized procurement model, a dedicated team handles all purchasing decisions. This approach offers several benefits, including economies of scale, standardized processes, enhanced negotiation power, and reduced risk. By consolidating purchasing power, organizations can negotiate better deals with suppliers and achieve significant cost savings. Additionally, standardized processes can improve quality control and compliance.
However, centralization can also lead to slower decision-making, a lack of local expertise, and reduced flexibility. In some cases, a centralized approach may not be able to adequately address the unique needs of different business units.
Decentralized Procurement
In a decentralized procurement model, purchasing decisions are made at the departmental or divisional level. This approach empowers individual teams to make timely decisions, fostering agility and responsiveness. Decentralization can also lead to a better understanding of local needs and requirements, enhancing customer satisfaction.
However, decentralization can result in inconsistencies, higher costs, and reduced control. Without strong governance and oversight, decentralized procurement can lead to duplication of efforts, suboptimal supplier relationships, and increased risk.
The Hybrid Approach
Many organizations have adopted a hybrid approach that combines the best of both worlds. This approach involves a centralized team that oversees strategic sourcing and risk management, while decentralized teams handle tactical purchasing decisions. By striking a balance between centralized control and decentralized flexibility, organizations can achieve optimal results.
The Role of Technology
Advanced procurement technologies, such as ERP systems and procurement software, play a crucial role in enabling both centralized and decentralized procurement. These tools can streamline processes, improve visibility, enhance collaboration, and support data-driven decision-making. By leveraging technology, organizations can overcome the challenges associated with both models and achieve greater efficiency and effectiveness.
Ultimately, the choice between centralized, decentralized, and hybrid procurement depends on an organization’s specific needs, culture, and strategic goals. By carefully considering these factors, organizations can select the approach that best aligns with their objectives and drives long-term success.
BONUS
A Real-World Example: ExxonMobil’s Centralized Procurement Strategy
A prime example of a company leveraging a centralized procurement strategy is ExxonMobil. As one of the world’s largest oil and gas companies, ExxonMobil has adopted a highly centralized procurement function.
By centralizing its procurement operations, ExxonMobil has been able to:
- Achieve significant cost savings: Through bulk purchasing and standardized contracts, the company has realized substantial cost reductions.
- Enhance negotiation power: A centralized procurement team can negotiate better deals with suppliers due to its increased bargaining power.
- Improve quality and consistency: Centralized procurement enables the company to enforce stringent quality standards and ensure consistent performance across all operations.
- Reduce risk: By consolidating procurement activities, ExxonMobil can better manage risks associated with supply chain disruptions and vendor performance.
- Foster innovation: A centralized procurement function can identify and implement innovative sourcing strategies, such as supplier collaboration and digital procurement tools.
While ExxonMobil’s centralized approach has yielded significant benefits, it’s important to note that no single model is perfect. The company likely employs a hybrid approach, combining centralized and decentralized elements to balance control, flexibility, and local responsiveness.
Other Oil and Gas Companies
Many other oil and gas companies, such as Shell, BP, and Chevron, have also adopted centralized procurement strategies to varying degrees. These companies recognize the importance of efficient and effective procurement in driving operational excellence and financial performance.
For better visibility 🙂
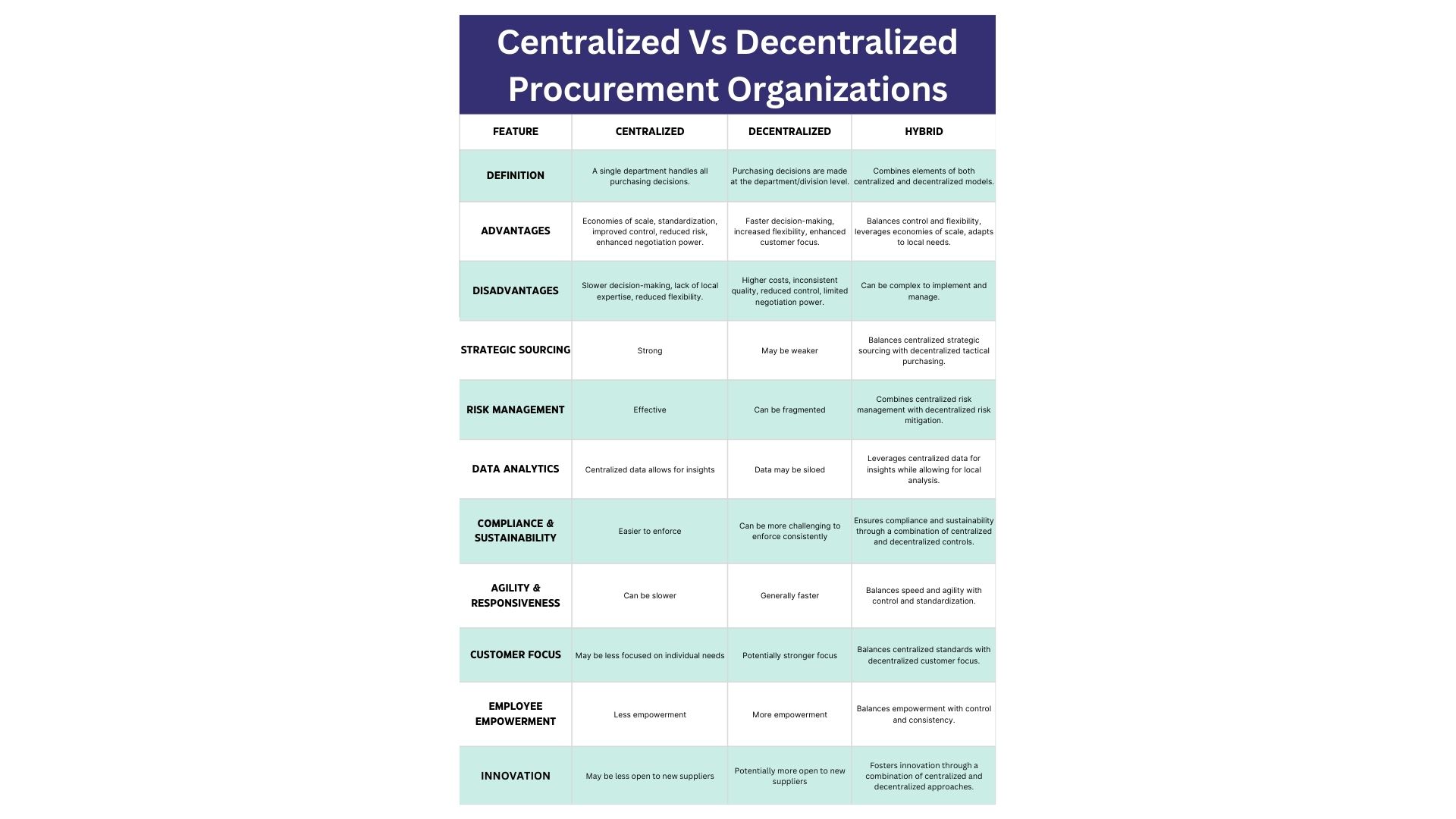
| Feature | Centralized Procurement | Decentralized Procurement | Hybrid Procurement |
| Definition | A single department handles all purchasing. | Purchasing decisions are made at the department/division level. | Combines elements of both centralized and decentralized models. |
| Advantages | Cost savings, standardization, improved control, reduced risk, enhanced negotiation power. | Faster decision-making, increased flexibility, enhanced customer focus. | Balances control and flexibility, leverages economies of scale, adapts to local needs. |
| Disadvantages | Slower decision-making, lack of local expertise, reduced flexibility. | Higher costs, inconsistent quality, reduced control, limited negotiation power. | Can be complex to implement and manage. |
| Strategic Sourcing | Strong | May be weaker | Balances centralized strategic sourcing with decentralized tactical purchasing. |
| Risk Management | Effective | Can be fragmented | Combines centralized risk management with decentralized risk mitigation. |
| Data Analytics | Centralized data allows for insights | Data may be siloed | Leverages centralized data for insights while allowing for local analysis. |
| Compliance & Sustainability | Easier to enforce | Can be more challenging to enforce consistently | Ensures compliance and sustainability through a combination of centralized and decentralized controls. |
| Agility & Responsiveness | Can be slower | Generally faster | Balances speed and agility with control and standardization. |
| Customer Focus | May be less focused on individual needs | Potentially stronger focus | Balances centralized standards with decentralized customer focus. |
| Employee Empowerment | Less empowerment | More empowerment | Balances empowerment with control and consistency. |
| Innovation | May be less open to new suppliers | Potentially more open to new suppliers | Fosters innovation through a combination of centralized and decentralized approaches. |
| Feature | Centralized Procurement | Decentralized Procurement | Hybrid Procurement |
| Definition | A single department handles all purchasing. | Purchasing decisions are made at the department/division level. | Combines elements of both centralized and decentralized models. |
| Advantages | Cost savings, standardization, improved control, reduced risk, enhanced negotiation power. | Faster decision-making, increased flexibility, enhanced customer focus. | Balances control and flexibility, leverages economies of scale, adapts to local needs. |
| Disadvantages | Slower decision-making, lack of local expertise, reduced flexibility. | Higher costs, inconsistent quality, reduced control, limited negotiation power. | Can be complex to implement and manage. |
| Strategic Sourcing | Strong | May be weaker | Balances centralized strategic sourcing with decentralized tactical purchasing. |
| Risk Management | Effective | Can be fragmented | Combines centralized risk management with decentralized risk mitigation. |
| Data Analytics | Centralized data allows for insights | Data may be siloed | Leverages centralized data for insights while allowing for local analysis. |
| Compliance & Sustainability | Easier to enforce | Can be more challenging to enforce consistently | Ensures compliance and sustainability through a combination of centralized and decentralized controls. |
| Agility & Responsiveness | Can be slower | Generally faster | Balances speed and agility with control and standardization. |
| Customer Focus | May be less focused on individual needs | Potentially stronger focus | Balances centralized standards with decentralized customer focus. |
| Employee Empowerment | Less empowerment | More empowerment | Balances empowerment with control and consistency. |
| Innovation | May be less open to new suppliers | Potentially more open to new suppliers | Fosters innovation through a combination of centralized and decentralized approaches. |

No responses yet